What is a Robot?
What is Robot?
Let us start by first answering the question/First things first: What exactly IS a robot?
When you hear the word ‘robot’, you think of the robots in Star Wars, Transformers (Autobots, roll out!), or in Terminator. However, in the real world, scientists have not been able to put as much sense into ‘robots’ as is shown in these movies. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t many robots around us. They are everywhere (maybe not as good-looking)!
So, if not them, then what IS a robot?
A robot, in simple words, is any machine designed to carry out a task. This would make you say, “Soooo, a calculator, a PC, a vacuum cleaner – all these are also robots?” Not exactly. Robots are machines that use programming to take decisions and carry out tasks. For e.g. a screwdriver is a machine because it carries out the task of fastening a screw, and reduces human effort (who knew defining a machine could be this simple?!). But it is not a robot. If we combine it with a robotic arm, then the entire thing can be called a robot.
Classification of Robots
A robot can be controlled by humans, either directly, or remotely, from a place far far away. Or a robot can take decisions, and work entirely on its own; such robots are called ‘autonomous robots’. There also exist robots that can move from one place to another; they are known as ‘mobile robots’. There are robots, autonomous robots, mobile robots, and then, there are autonomous mobile robots. The last two are what we will be making later in this course.
Application of Robots
Most of the work that the robots do is either dangerous (looking for bombs, anyone?), or back-breaking, or nasty; if not one of these, then boring (poor Rosie Jetson). But that is not true always. Today, robots can make music, can paint, and can play football! Rest assured, the ones that you’ll be making are definitely going to be cool!

We can find robots in a multitude of fields – right from cleaning your home to celebrating birthdays on Mars. Jokes apart, in the modern world, robot has found a place in almost every field. Some of their endless applications are given below:
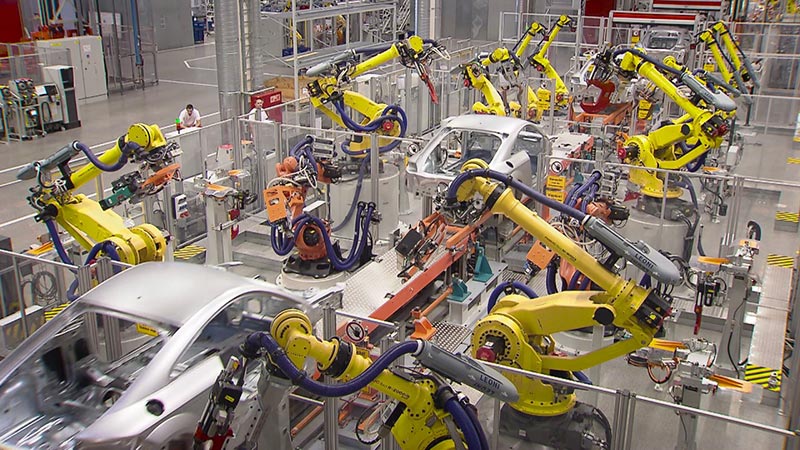
- Industry: For handling and moving materials from one place to another, and for other purposes such as painting, manufacturing, welding, etc.
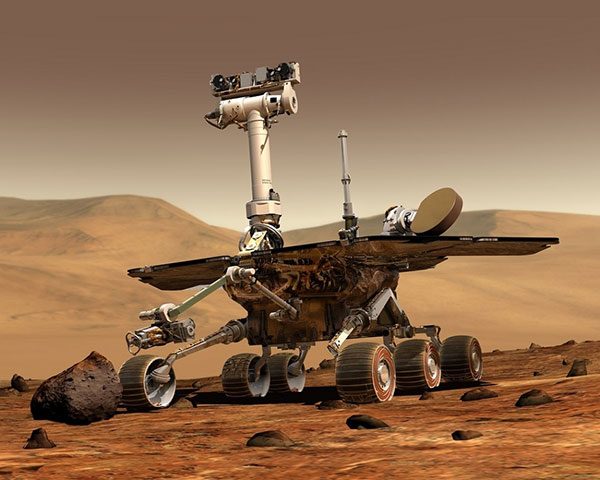
- Space: For exploring outer space. E.g., the Curiosity Rover
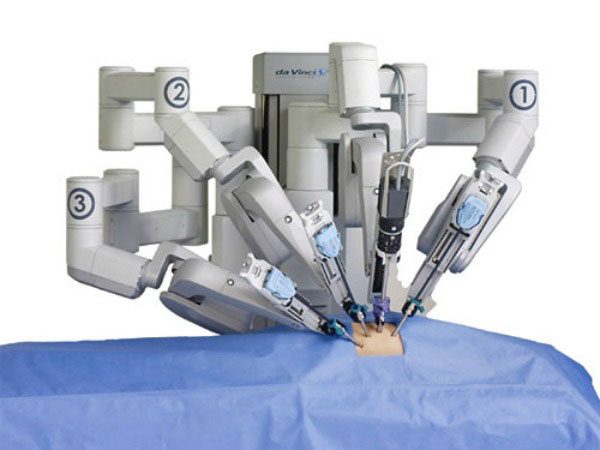
- Hospitals: Surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, pharmacy robots, etc.
- Transportation: Self-driving cars, transportation of goods and services, etc.
- Agriculture: For tasks such as vegetable and fruit picking.
- Military: Bomb discarding robots, drone explorations, etc.
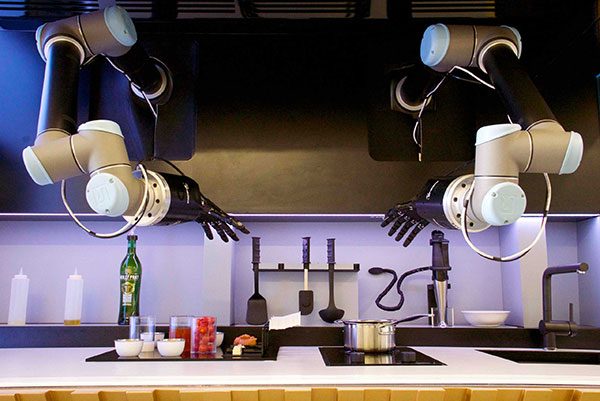
- Households: For cooking, cleaning, and washing purposs.
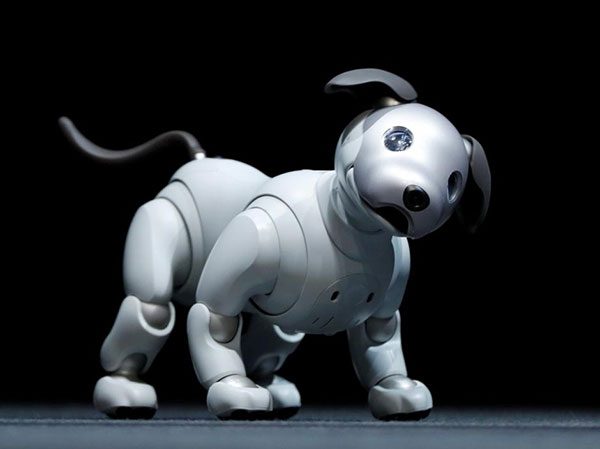
- Entertainment: Humanoids, robot dogs, mobile phones, computers, etc. E.g. Aibo the robot dog.